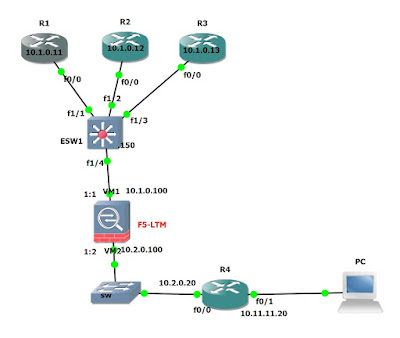
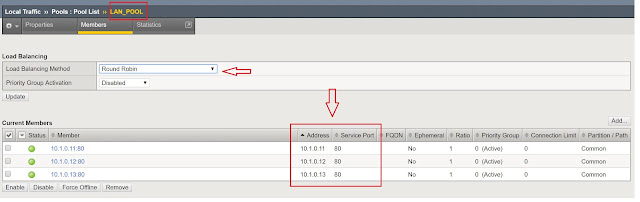
F5-LTM useful CLI commands to Troubleshoot
We will be working with shell mode, for shell mode type “tmsh” and hit enter. You will go to BIG IP shell mode.
Below are few cli commands used to perform basic troubleshooting in LTM to check Client-Server Connections.
Step1:
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#ping <Server ip address> -I <source_self_IP>
Step2:
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#telnet <Server ip address> <portnumber>
Step3:
Try to access server directly from your local PC using direct server/Node ip address, this is just to check if there is any issue with the server or not.
Step4:
Test access to servers from LTM CLI, do 'quit' to exit from tmos shell mode
[root@rajiv:Active:Standalone] log #curl -v http://<Virtual Server IP>
[root@rajiv:Active:Standalone] log #curl -v https://<Virtual Server IP>
Step5:
check the list of Active connections, if require you can also delete Existing/old connections using below commands.
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)# show /sys connection cs-server-addr <VIRTUAL-SERVER-IP-ADDRESS>
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)# delete /sys connection cs-server-addr <VIRTUAL-SERVER-IP-ADDRESS>
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#show /sys connection cs-client-addr <CLIENT-IP-ADDRESS>
tmsh show /sys connection ss-server-addr <NODE-IP-ADDRESS> ss-server-port <NODE-PORT-NUMBER>
for Example:
client--->VIP(LTM)Selfip--------->SERVER
cs-client-addr----->client pc ip address
cs-server-addr----->LTM Virtual Server IP address
ss-client-addr------>LTM Self IP
ss-server-addr------>Server IP address
cs-client-port---->Clinet source port number
cs-server-port----->Client Destination port number
ss-client-port----->LTM source port
ss-server-port----->LTM destination port
Step6:
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#tcpdump -i <vlanname> host <ipaddress> and port <portnumber> -w /var/tmp/capture1.pcap
OR
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#tcpdump src host <ipaddress> and dst host <ipaddress> and dst port <portnumber>
Optional:-
-i <interface number> --->Interface such as 1:1 ,2:1
-i <vlan name>
-i 0.0 ---->captures on all interfaces.
-ni ---->disables name resolution
-w <capture1.pcap>----->captures the traffic to a file.
Step7:
Check LTM logs you can find it in System››Logs : Local Traffic or
[root@rajiv:Active:Standalone] log #cd /var/log/
[root@rajiv:Active:Standalone] log #cat ltm
or
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#show /sys log ltm
or
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#show /sys log <log> range <date range>
For example, to view ltm logs from three days ago until now, type the following command:
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#show /sys log ltm range now-3d
For example, to view all ltm logs from 2019-03-05, type the following command:
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#show /sys log ltm range 2019-03-05
For example, to view ltm logs from two to four days ago, type the following command:
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#show /sys log ltm range now-2d--now-4d
For example, to view ltm logs from 2019-03-02 through 2019-03-05, type the following command:
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#show /sys log ltm range 2019-03-02--2019-03-05
Step1:
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#ping <Server ip address> -I <source_self_IP>
Step2:
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#telnet <Server ip address> <portnumber>
Step3:
Try to access server directly from your local PC using direct server/Node ip address, this is just to check if there is any issue with the server or not.
Step4:
Test access to servers from LTM CLI, do 'quit' to exit from tmos shell mode
[root@rajiv:Active:Standalone] log #curl -v http://<Virtual Server IP>
[root@rajiv:Active:Standalone] log #curl -v https://<Virtual Server IP>
Step5:
check the list of Active connections, if require you can also delete Existing/old connections using below commands.
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)# show /sys connection cs-server-addr <VIRTUAL-SERVER-IP-ADDRESS>
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)# delete /sys connection cs-server-addr <VIRTUAL-SERVER-IP-ADDRESS>
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#show /sys connection cs-client-addr <CLIENT-IP-ADDRESS>
tmsh show /sys connection ss-server-addr <NODE-IP-ADDRESS> ss-server-port <NODE-PORT-NUMBER>
for Example:
client--->VIP(LTM)Selfip--------->SERVER
cs-client-addr----->client pc ip address
cs-server-addr----->LTM Virtual Server IP address
ss-client-addr------>LTM Self IP
ss-server-addr------>Server IP address
cs-client-port---->Clinet source port number
cs-server-port----->Client Destination port number
ss-client-port----->LTM source port
ss-server-port----->LTM destination port
Step6:
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#tcpdump -i <vlanname> host <ipaddress> and port <portnumber> -w /var/tmp/capture1.pcap
OR
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#tcpdump src host <ipaddress> and dst host <ipaddress> and dst port <portnumber>
Optional:-
-i <interface number> --->Interface such as 1:1 ,2:1
-i <vlan name>
-i 0.0 ---->captures on all interfaces.
-ni ---->disables name resolution
-w <capture1.pcap>----->captures the traffic to a file.
Step7:
Check LTM logs you can find it in System››Logs : Local Traffic or
[root@rajiv:Active:Standalone] log #cd /var/log/
[root@rajiv:Active:Standalone] log #cat ltm
or
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#show /sys log ltm
or
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#show /sys log <log> range <date range>
For example, to view ltm logs from three days ago until now, type the following command:
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#show /sys log ltm range now-3d
For example, to view all ltm logs from 2019-03-05, type the following command:
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#show /sys log ltm range 2019-03-05
For example, to view ltm logs from two to four days ago, type the following command:
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#show /sys log ltm range now-2d--now-4d
For example, to view ltm logs from 2019-03-02 through 2019-03-05, type the following command:
root@rajiv(Active)(/Common)(tmos)#show /sys log ltm range 2019-03-02--2019-03-05